Taxability of Restaurants Under GST Composition Scheme
The GST Composition Scheme is a simplified tax scheme designed for small businesses with an annual turnover of up to ₹1.5 crore. Under this scheme, companies must pay a fixed percentage of their turnover as tax without needing to maintain detailed records or file regular returns.
BOOK A FREE DEMO
However, the taxability of restaurants under the GST composition scheme can be complex and requires careful consideration of various factors, including the type of restaurant and the services provided. In this context, it is essential to understand the GST law’s relevant provisions to determine the composition scheme applicable to restaurants.
Also Know About – Differences Between Regular and Composite Schemes

GST Rates for Restaurant Bills (Starting From January 2019)
The table below provides a comprehensive overview of the applicable GST rates for different types of restaurants and food-related services in India. Below are the GST rates for restaurant bills.
| Type Of Restaurants | GST Rates |
| Railways/IRCTC | 5% (ITC is not available) |
| All standalone restaurants | 5% (ITC is not available) |
| Standalone outdoor catering services | 5% (ITC is not available) |
| Dining facilities in hotels where the room tariff is less than ₹7,500 per night. | 5% (ITC is not available) |
| Normal or composite outdoor catering within Hotels where the room tariff is less than ₹7,500 per night. | 5% (ITC is not available) |
| A restaurant that is within a hotel where the room tariff is greater than or equivalent to ₹7,500 per night. | 18% (ITC is available) |
| Outdoor catering (normal or composite) within hotels where the room tariff is greater than or equivalent to ₹7,500 per night) | 18% (ITC is available) |
Note that, in the case of restaurants operating within hotels and those operating outdoor catering services within hotels, the GST rates, as mentioned in the table, apply only to the dining and catering services provided within the hotels. The accommodation within the hotel is not subject to the same GST rates.
GST Composition Scheme Rules For Restaurants
Restaurants must comply with the composition scheme’s requirement to charge GST at a special rate of 5% of turnover, subject to the following limitations.
- Not to exceed 1.5 crores in turnover (₹1 Crore in case of particular category state)
- Should only work in restaurants (a special exemption has been made for services like interest and exempt services).
- Restaurants are unable to produce goods for interstate export.
- Cannot provide any goods that are not GST-taxable, such as alcohol.
- They are unable to do so by using an online retailer.
- There is no input tax credit available to restaurants.
- They cannot collect taxes from the customer
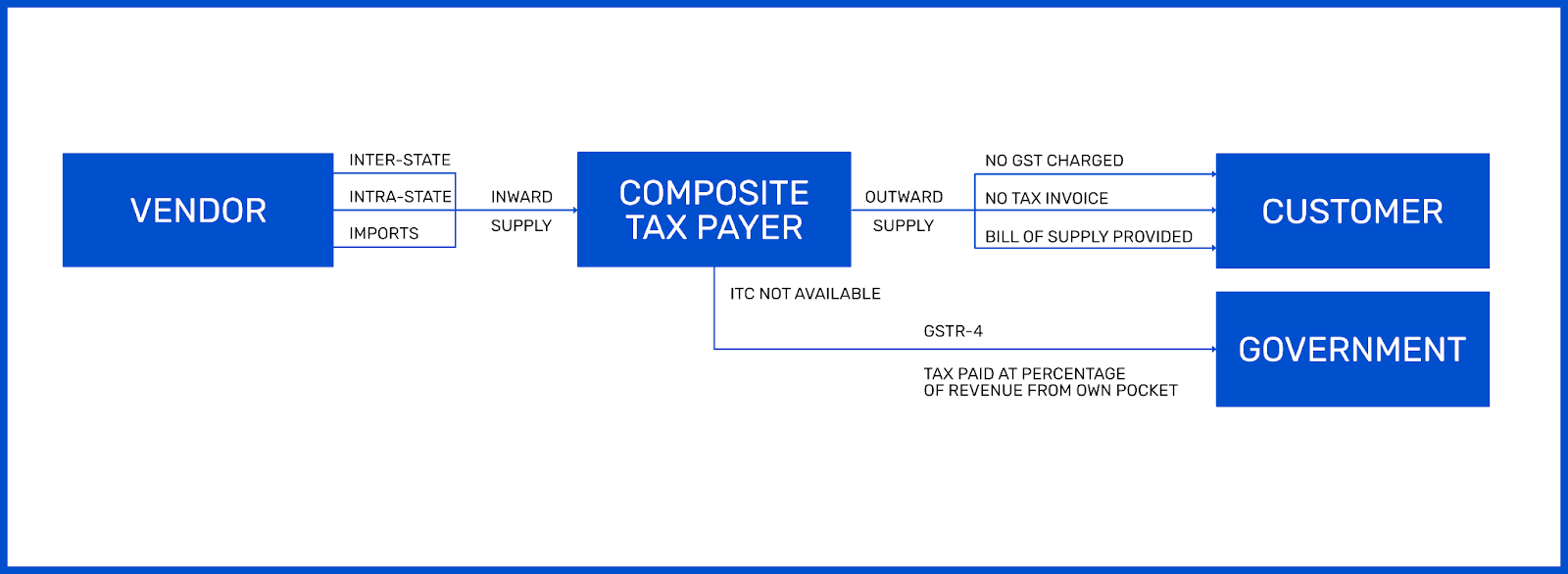
Regular Tax Payer V/s Composition Dealer
| Particulars | Regular Tax Payer | Composite Tax Payer |
| Registration | Threshold Limit – ₹20 L | Threshold Limit – ₹1.5 Cores |
| Territory Of Business | No Restriction On Supply | Limited To Intra-State Supply |
| Change between regular and composition, or vice versa | Compliance Procedure Is High | Once It Crosses The Limit, Compulsory Registration Under Regular Provisions. |
| Input Tax Credit | Depends On The Category | Not Entitled To Avail The Credit |
| Business Through e-commerce | Can Supply Goods Through E-Commerce | Cannot supply Goods Through E-Commerce |
| Tax Collection | Allowed To Collect Tax From The Buyer | Cannot Collect Tax From The Buyer |
| Tax Invoice | Can raise a tax invoice for outward supply | Can Raise Bill Of Supply Instead Of Tax Invoice For Outward Supply |
| GST Returns | Monthly GSTR-1 and GSTR-3B | Quarterly – Only GSTR 4 |
Identify Restaurants Under the Composition Scheme
- Restaurants that choose the composition scheme must state at the top of the bill of supply, “Composition taxable person, not eligible to collect tax on supplies.”
- Every notice or signboard prominently displayed at their place of business must also include a description of the words that comprise the phrase “taxable person.”
Restaurant GST Rate
Understanding restaurant’s GST rates is crucial for business owners and customers. The Goods and Services Tax (GST) simplifies the taxation process, but it’s essential to know the specific rates that apply to different types of restaurants.
Standard GST Rates for Restaurants
- Non-AC Restaurants:The GST rate for non-AC restaurants is 5% without the benefit of input tax credit (ITC). This means that restaurants cannot claim credit for the taxes paid on their inputs while the tax rate is lower.
- AC Restaurants:Restaurants with air conditioning are also taxed at 5% GST without ITC. The exact rate applies to restaurants within hotels where the room tariff is less than ₹7,500 per night.
- Outdoor Catering:The GST rate for outdoor catering services is 18%, with the benefit of ITC.
GST Composition Scheme for Restaurants
Restaurants can opt for the composition scheme if their turnover is up to ₹1.5 crore. Under this scheme, the GST rate is 5%, but they cannot avail of the input tax credit. This simplified scheme helps small restaurant businesses by reducing their tax compliance burden.
Why Understanding GST Rates Matters?
Knowing the applicable GST rates helps restaurant owners price their menus correctly and ensures they comply with tax regulations. Understanding these rates allows customers to see the tax component in their bills.
Business owners and patrons can more effectively navigate the taxation landscape by tracking the restaurant GST rate and the composition scheme.
Download: Free GST Accounting Software For PC
Benefits To Restaurants Under GST
- Need to be compliant with only one law instead of multiple laws
- Pastry manufacturing excise, lodging and restaurant service tax, restaurant VAT, opulence rental tax, and entertainment tax on ticketed events.
- Allowed to claim credit for GST paid for procurements
- Before GST, restaurant operators could not claim credit for entry tax paid on machinery, CST paid on interstate purchases, excise paid on furniture purchases, or CST paid on packaged food sales. In the case of GST, all taxes paid on such purchases are creditable unless they are required to pay taxes at a reduced rate.
- 5% composition & tax payment plan options are available if the turnover is less than ₹1.5 crores.
- 5% concessional rate (but input tax credit is not available)
- Credit for outdoor catering or food, but only when used in a business line similar to restaurants.
Conclusion
The taxability of restaurants under the GST composition scheme can be complex and requires careful consideration of various factors. While the scheme can offer certain benefits for small restaurants, it may not be suitable for all businesses in this sector. Therefore, it is essential to seek professional advice and assess the specific requirements and circumstances of the restaurant business before opting for the GST composition scheme.
Streamline your restaurant operations with BUSY GST Billing Software.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the current restaurant GST rate in India?The current restaurant GST rate in India is 5% for restaurants that do not provide alcohol. This rate applies to air-conditioned and non-air-conditioned restaurants, including hotels with tariffs of less than ₹7,500 per night.
-
How is the GST rate for restaurant services determined?The type of service provided determines the GST rate for restaurant services. Tax authorities levy a 5% tax on standalone restaurants without allowing input tax credits. Tax authorities apply an 18% tax rate with an input tax credit to restaurants in hotels charging ₹7,500 or more per night.
-
What does GST for restaurant services cover?GST for restaurant services covers the supply of food, beverages, and other services. It includes dine-in and takeaway services, ensuring the hospitality industry applies a standardised tax rate.
-
Is there a particular restaurant GST rate composition scheme available?The restaurant GST rate composition scheme allows small restaurants to pay a fixed 5% GST on their sales. They do not receive input tax credits. It simplifies compliance for small businesses.
-
Who qualifies for the composition scheme for restaurant businesses?The composition scheme for restaurant businesses is available to those with an annual turnover of up to ₹1.5 crore. This scheme allows restaurants to pay a lower % GST rate of 5% on their turnover, simplifying the tax filing process.
-
How does GST for hotels and restaurants differ based on tariffs?Hotels and restaurants have varying GST rates based on room tariffs. Restaurants in hotels with room rates below ₹7,500 per night charge 5% GST. Hotels with room rates of ₹7,500 or above charge 18% GST, which includes input tax credit provisions.
-
What is the applicable GST on hotels and restaurants?The GST on hotels and restaurants is 5% for standalone restaurants and hotels with room rates below ₹7,500 per night. For restaurants in hotels with room tariffs of ₹7,500 or above per night, the GST rate is 18%.
-
How does the government apply GST on different types of restaurant services?The GST on restaurant services is 5% for all food and drinks. This applies whether you eat in, take out, or get delivery. The only exception is if the items include alcohol. It ensures consistency in tax rates across the service spectrum.
-
What is the hotel restaurant GST rate for luxury hotels?The hotel restaurant GST rate for luxury hotels, where room tariffs are ₹7,500 per night, is 18%. This rate applies to all restaurant services within such hotels and allows them to claim input tax credits.
-
How do I determine the restaurant GST percentage applicable to my business?To determine the restaurant GST percentage applicable to your business, consider the type of service and your turnover. Restaurants and hotels with room rates under ₹7,500 per night have a 5% GST rate. Those with rates above ₹7,500 have an 18% rate and can claim input tax credit.
