Different Types of Json Errors While Filing GSTR-9C
BOOK A FREE DEMO
Definition of GSTR-9C
GSTR-9C is a reconciliation statement that businesses in India must file annually as part of their GST return (GSTR-9). It is a certification of the reconciliation between the data declared in the annual return (GSTR-9) and the books of accounts maintained by the taxpayer.
In addition to the GSTR-9C audit form, the taxpayer must complete the reconciliation statement and obtain certification from an auditor. It must be certified by a professional accountant and failure to file it can result in penalties.
Who needs to file GSTR-9C
GSTR-9C is a reconciliation statement that needs to be filed by businesses registered under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India. The company must have a turnover of more than Rs. 2 crores in the financial year for which the return is being filed. All businesses must file the GSTR-9 return and the reconciliation statement (GSTR-9C) annually, along with certification from a Chartered Accountant or a Cost Accountant.
Significance of GSTR-9C in GST
GSTR-9C is important in the Goods and Services Tax (GST) system in India for several reasons:
- Compliance: Filing GSTR-9C is a mandatory requirement for businesses registered under GST and non-compliance can result in penalties and legal consequences.
- Reconciliation of Data: The GSTR-9C reconciliation statement provides a detailed comparison between the data declared in the annual return (GSTR-9) and the books of accounts maintained by the taxpayer. This ensures that the information declared in the return is accurate and complete.
- Transparency: The certification by a Chartered Accountant or a Cost Accountant assures the Indian government that the reconciliation has been properly conducted and that the information declared in the return is accurate. This enhances the transparency and accountability of the GST system.
- Detection of Errors: The reconciliation process helps in detecting any errors or discrepancies in the data declared in the return and the books of accounts, and provides an opportunity to correct them.
- Maintenance of Records: GSTR-9C serves as an important record-keeping tool for businesses and helps in maintaining accurate records for tax purposes.
In summary, GSTR-9C is an important aspect of the GST system in India as it promotes compliance, ensures the accuracy of data, enhances transparency, helps detect errors, and supports record-keeping.
Get a Free Trial – Best Accounting Software For Small Business
Format of GSTR-9C
There are two parts to registering for GSTR-9C:
- Reconciliation Statement (Part A)
- Auditor Certification (Part B)
Part A – Reconciliation Statement
Part A of GSTR-9C is further divided into 5 parts, as below:
- Basic Details
- Reconciliation of turnover declared in audited Annual Financial Statement with turnover declared in Annual Return (GSTR-9)
- Reconciliation of Tax Paid
- Reconciliation of Input Tax Credit
- Auditor’s recommendation on additional liability due to non-reconciliation
Let’s discuss each part in detail
Part I – Basic Details
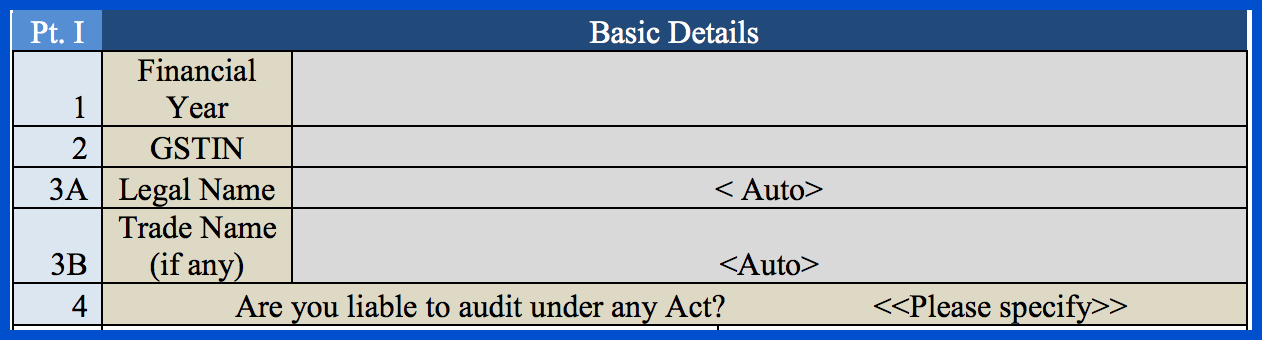
In this part of GSTR-9C, you need to input basic information like the financial year, your GSTIN, your legal and trade names, and whether or not you are liable to be audited under the provisions of any Act.
Part II – Reconciliation of turnover declared in audited Annual Financial Statement with turnover declared in Annual Return (GSTR-9)
This section is further subdivided into four sections:
- Section 5
- Section 6
- Section 7
- Section 8
Section 5 is where you need to input information pertaining to reconciliation of the gross turnover of your business. It requires the following information:
- The turnover, which includes exports and is stated in the audited financial reports for the State.
- The revenue that hasn’t been billed yet, which was recorded at the start of the financial year.
- Any advances that have not been adjusted by the end of the financial year.
- The supply that is considered to have taken place, as per Schedule I.
- All credit notes issued after the end of the financial year, but reflected in the annual return.
- Trade discounts that were accounted for in the audited annual financial statement but are not allowed under GST.
- The turnover for the period ranging from April to June 2017.
- The revenue that hasn’t been billed yet, which is calculated for the end of the financial year.
- Any advances that have not been adjusted at the beginning of the financial year.
- Credit notes that were accounted for in the audited annual financial statements but are not allowed under GST.
- Any adjustments made due to the supply of goods by SEZ units to DTA units.
- The turnover for the period under the composition scheme.
- Any adjustments in turnover under Section 15.
- Any adjustments in turnover due to foreign exchange fluctuations.
- Any adjustments in turnover for reasons not listed above.
- The annual turnover after considering all the adjustments mentioned above. This field is automatically populated.
- The turnover declared in the annual return, GSTR-9.
- The un-reconciled turnover, which is calculated as the difference between lines P and Q above. (Q – P)

Section 6 is where you must enter the possible reasons for any unreconciled differences in the gross annual turnover of your business.
Get a Free Demo – Best Billing and Invoicing Software

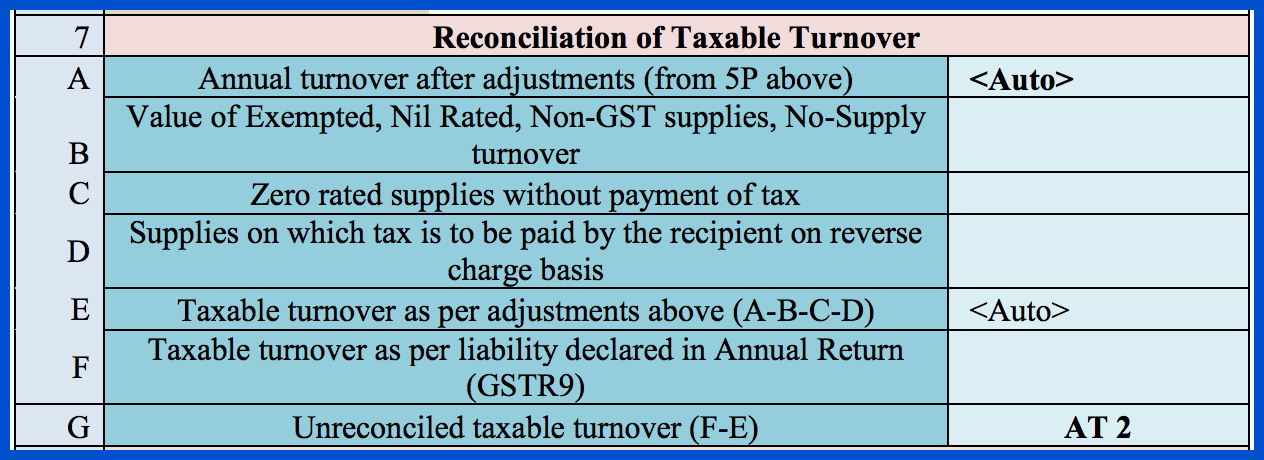
Section 7 is where you need to enter information pertaining to the reconciliation of taxable turnover. It requires the following information:
- The annual turnover after all adjustments have been made. This value is filled in automatically.
- The combined value of exempted, nil rated, non-GST supplies, and no-supply turnover.
- The value of supplies that are zero-rated, and for which no tax was paid.
- The value of supplies for which the recipient has to pay tax under reverse charge.
- The taxable turnover as per the adjustments made in the lines above. (A – B – C – D)
- The taxable turnover concerning the liability stated in the annual return (GSTR-9).
- The value of unreconciled taxable turnover. (F – E)
Section 8 is similar to Section 6, as here you need to enter the possible reasons for any unreconciled differences between the taxable turnover that you declared in your annual return and the one derived from Section 7, line E.

Part III – Reconciliation of Tax Paid
In Part 3 of GSTR 9C, you need to enter information about the taxes you have paid. Part 3 is further subdivided into 3 sections:
- Section 9
- Section 10
- Section 11
Section 9 is where you need to enter the taxable value, the central and state taxes, integrated taxes, and cess values applicable for each of the following tax rates:
- 5%
- 12%
- 18%
- 28%
- 3%
- 0.25%
- 0.10%
For each of the above tax rates, the tax paid through reverse charge should be listed on a separate line from the tax that was collected as per the normal mechanism.

Section 10 is where you need to provide the possible reasons for any differences between the total tax amount you have paid as per your reconciliation statement and the total tax paid as was reported in your annual return (GSTR-9).
Get a Free Trial – Best GST Accounting Software For Small Business

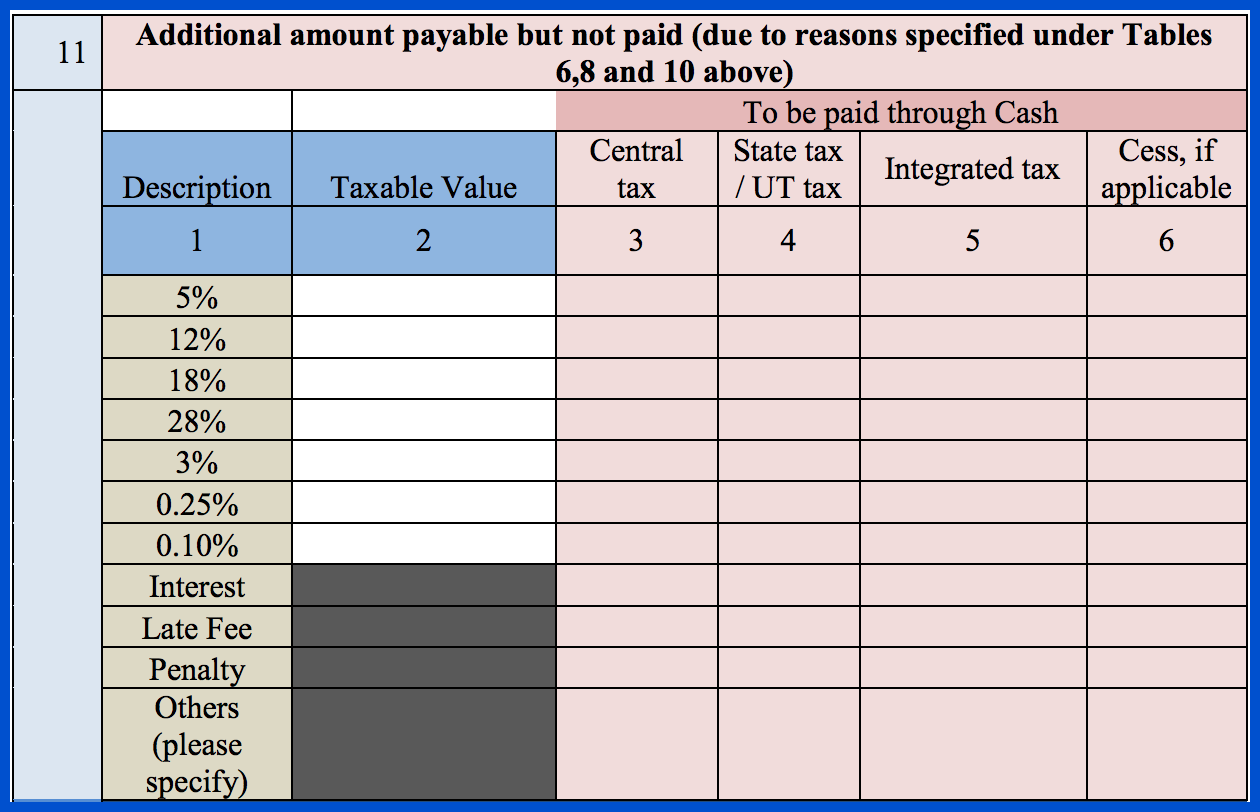
Section 11 is where you need to provide the details of any taxes that are due but have not yet been paid, as a result of the reasons mentioned above in Sections 6, 8, and 10.
Part IV – Reconciliation of Input Tax Credit
Part 4 of the form deals with reconciling Input Tax Credit (ITC). It is subdivided into 5 sections:
- Section 12
- Section 13
- Section 14
- Section 15
- Section 16
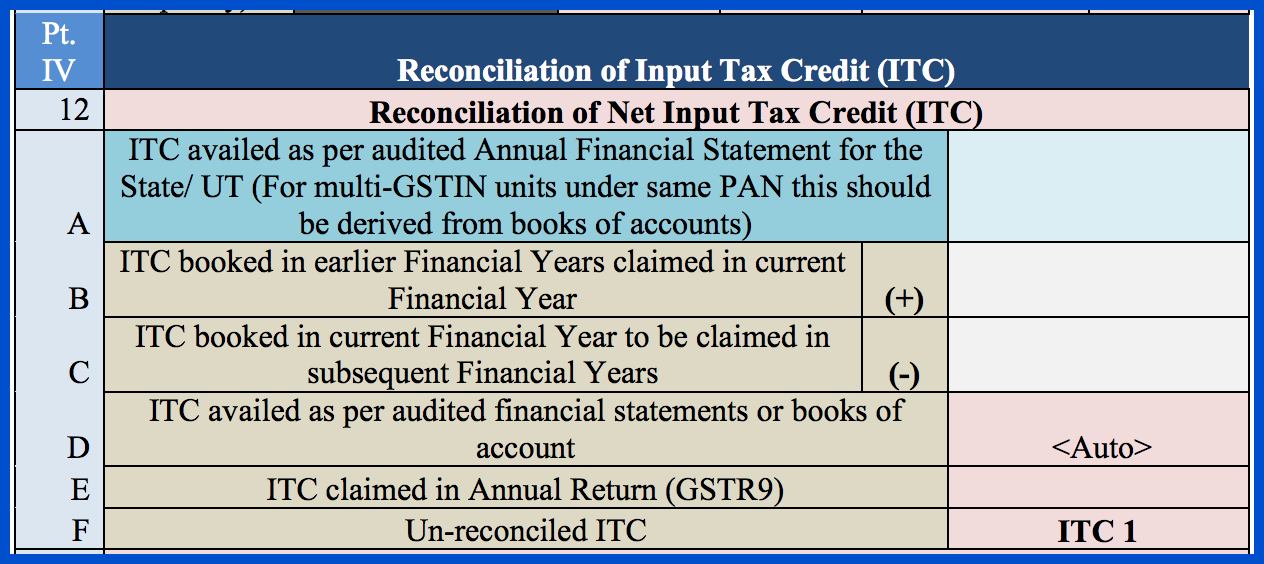
In Section 12, you need to provide information about the ITC availed in the following categories:
- ITC availed as per the audited annual financial statement for the state or UT. If you have multiple GSTINs under the same PAN, you must derive this value from the audited accounts.
- ITC mentioned in the accounts for earlier financial years but availed in the current financial year.
- ITC mentioned in the accounts of the current financial year but kept to be availed in the next financial year.
- ITC that has been availed as per the audited financial statements or accounts. This field will be auto-populated.
- ITC claimed in your annual return (GSTR-9).
- Un-reconciled ITC.
In Section 13, you need to enter the possible reasons for any differences that occur between the Input Tax Credit that you have claimed in your annual return, and that which you have claimed in your audited financial statements.

In Section 14, you need to enter the value for each category of expenses, the amount of total Input Tax Credit claimed for each category, and the amount of eligible Input Tax Credit that is availed for each category. The total amount of eligible ITC availed shall be calculated automatically based on the input numbers.

Section 15 lets you provide possible reasons for any difference between the total amount of ITC availed (Section 14, Line R), and the ITC availed as per your filed annual return (Section 14, Line S).

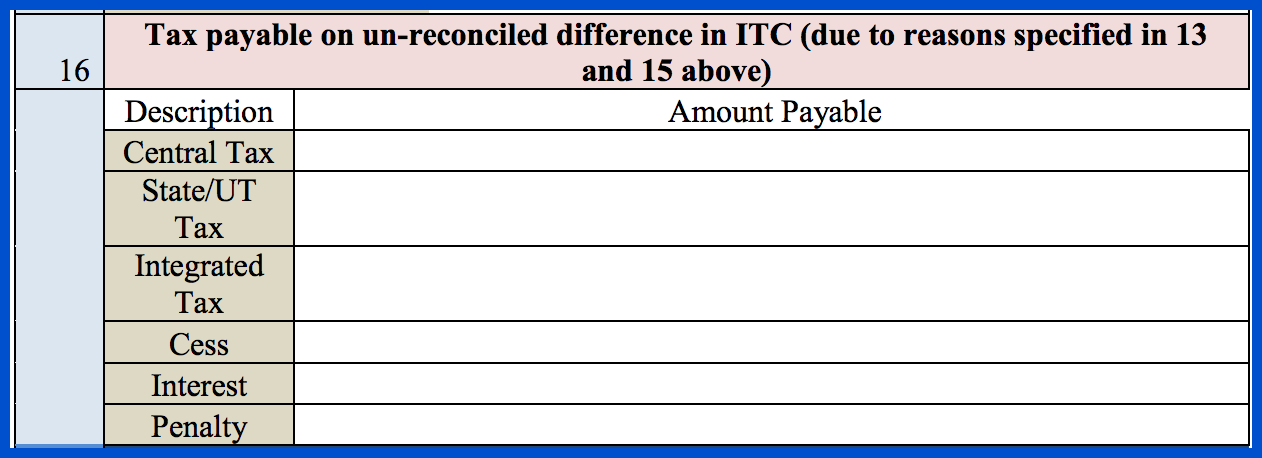
In Section 16, you need to enter the following information pertaining to any unreconciled differences as per Section 13 and Section 15:
- Central Tax
- State or Union Territory Tax
- Integrated Tax
- Cess
- Interest
- Penalty
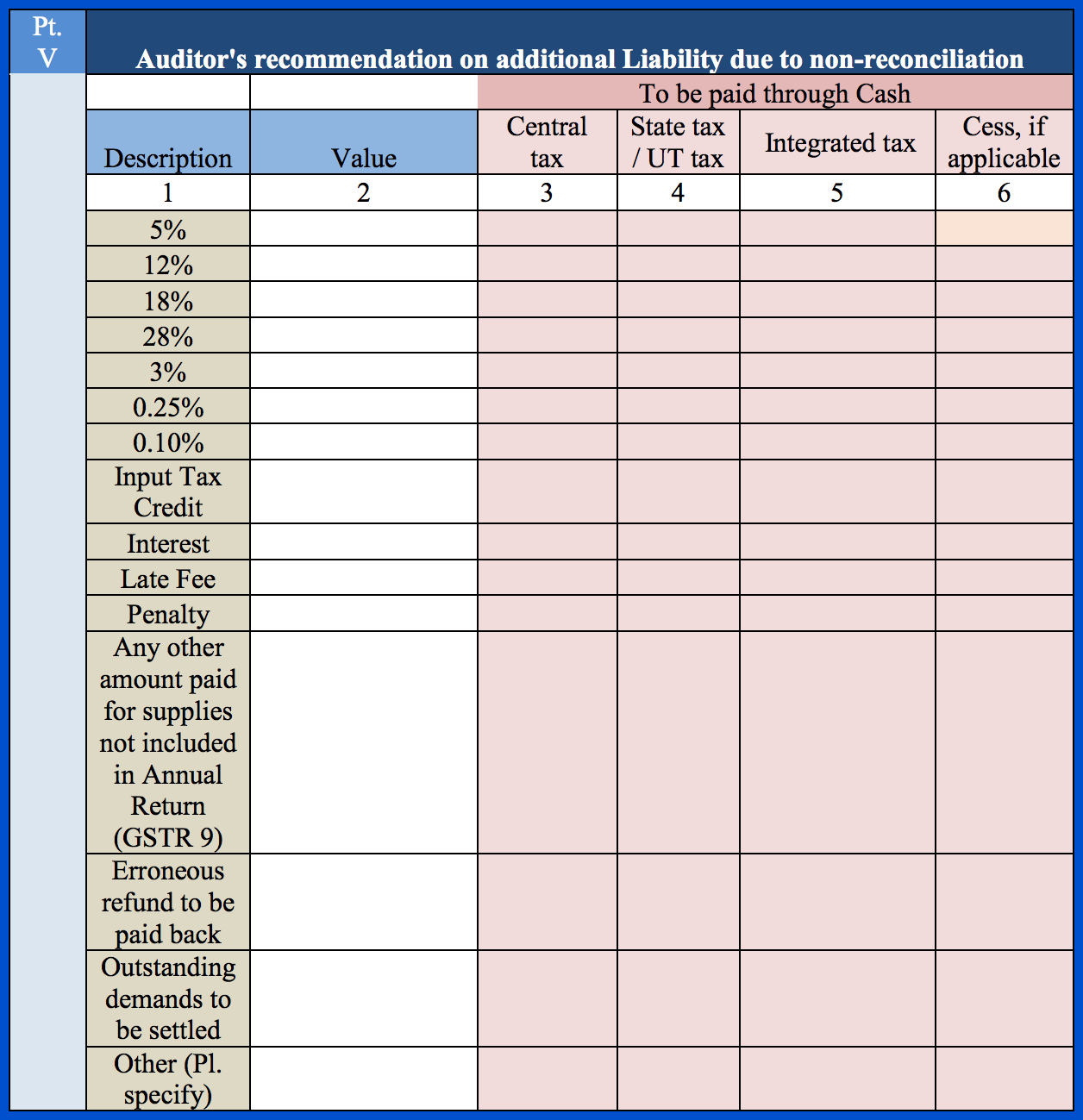
Part V – Auditor’s recommendation on additional liability due to non-reconciliation
Part 5 of GSTR 9C is to be filled by the auditor. Here, they can provide any recommendations on any additional tax liability due to non-reconciliation. They need to enter the taxable value, central and state tax, integrated tax, and cess value (if applicable) for various categories, including the following individual tax rates:
- 5%
- 12%
- 18%
- 28%
- 3%
- 0.25%
- 0.10%
Apart from the above, they need to enter the applicable input tax credit (ITC), interest, late fees, penalties, any other amounts that were paid but were not included in GSTR-9, any erroneous refunds that need to be paid back, and any outstanding demands that need to be settled.
Explore a Free Demo of – Best Inventory Management Software For Small Business
To file GSTR-9C, you need to sign and authenticate the return either using a digital signature certificate (DSC) or through your Aadhaar-based signature.

Part B – Auditor Certification
Being auditor certified in GSTR-9C means that a Chartered Accountant or a Cost Accountant has reviewed and certified the reconciliation statement filed as part of the annual GSTR-9 return by a business registered under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India. The certification confirms the precision and completeness of the reconciliation between the data declared in the annual return (GSTR-9) and the books of accounts maintained by the taxpayer. The certification assures the Indian government that the reconciliation has been appropriately conducted and that the information declared in the return is accurate. Failure to obtain the certification can result in penalties and legal consequences.

Documents for filing GSTR-9C
The following documents are required for filing GSTR-9C:
- Books of accounts (ledgers, balance sheets, profit and loss statements, etc.)
- Purchase and sales invoices
- GST returns (GSTR-1, GSTR-2, GSTR-3) filed during the financial year
- Bank statements and other financial documents that support the entries in the books of accounts
- Certification from a Chartered Accountant or a Cost Accountant

These documents are needed to prepare the reconciliation statement which is a part of the GSTR-9C filing. The reconciliation statement compares the data declared in the GST returns with the books of accounts and ensures that the information declared is accurate and complete.
Download GSTR-9C
There are two ways to download GSTR-9C: online and offline.
Online Method:
- Go to the GST portal.
- Log in with your username and password.
- On the dashboard, click the “Annual Return” tab.
- Choose the relevant fiscal year.
- Click “Initiate e-filing” and file the GSTR-9 form first before filing the reconciliation form.
Offline Method:
- Go to the GST portal.
- Select “Downloads” and go to “Offline Tools.”
- Find the GSTR-9C Offline Tool.
- Download the tool and extract the zip file.
- Enable the editing and content option.
- Read the “Read Me” tab.
- Fill in the basic details on the “Home” page like GSTIN, fiscal year, trade name, legal name, and Act.
- Confirm your choice when prompted and save the data before closing the tool.
Frequency of Filing
GSTR-9 and GSTR-9C must be filed annually together with a deadline of December 31st of the following financial year. For instance, the deadline for the financial year 2021-22 is December 31, 2022.
Consequences of Non-Filing
The consequences of non-filing of GSTR-9C in India can include:
- Financial penalties: Late fees or penalties may be imposed for failing to file the GSTR-9C return on time.
- Legal action: The government may take legal action against businesses that do not comply with the filing requirements for GSTR-9C.
- Disruptions to business operations: Non-compliance with the filing requirements for GSTR-9C can result in disruptions to a business’s operations, such as frozen bank accounts, seizure of assets, and other enforcement actions.
- Loss of credibility: Failure to file the GSTR-9C return on time can damage a business’s reputation and credibility in the eyes of suppliers, customers, and the government.
- Missed opportunities: Failing to file the GSTR-9C return can result in missed opportunities to claim input tax credits or other benefits available under the GST regime.
Importance of accurate reconciliation of data
Accurate reconciliation of data in GSTR-9C is important because it helps ensure the correctness and completeness of the information declared in the annual return (GSTR-9) and the books of accounts maintained by the taxpayer.
The reconciliation statement and certification by an auditor assure the Indian government that the data declared in the return is accurate and that the reconciliation has been appropriately conducted.
Inaccurate reconciliation can result in penalties and legal consequences, so it is important to ensure that the reconciliation statement is accurate and properly certified.
List of JSON Errors in GSTR-9C Filing & Solutions
During the GSTR-9C filing, taxpayers may encounter various JSON errors. Here are common errors and their solutions:
- “File Corrupted” Error:
- Cause: The JSON file may have been corrupted during generation or upload.
- Solution: Regenerate the JSON file using the correct format and try uploading it again.
- “Invalid Format” Error:
- Cause: The structure of the JSON file is incorrect.
- Solution: Ensure the JSON file is generated using the latest software version and check its structure against the GST portal’s validation requirements.
- “Mismatch in Data” Error:
- Cause: Discrepancy between the data in the GSTR-9C and the data uploaded in GSTR-3B.
- Solution: Reconcile all figures, especially tax liabilities, and make sure both GSTR-9C and GSTR-3B match before filing.
- “Error in Digital Signature Validation” Error:
- Cause: The DSC used may not be valid or properly linked.
- Solution: Check the validity of your DSC and ensure it is correctly registered with the GST portal.
- “File Upload Failed” Error:
- Cause: Network or server issues.
- Solution: Retry uploading after some time or check your internet connection.
- “Field Length Exceeded” Error:
- Cause: The data entered exceeds the field’s character limit.
- Solution: Review and shorten the data fields that exceed the length requirement.
- “JSON File Not Readable” Error:
- Cause: The file may not be in the correct format or is corrupted.
- Solution: Regenerate the JSON file and ensure it is compatible with the portal.
- “JSON Generation Error”:
- Cause: Errors in the software while generating the JSON file.
- Solution: Use updated software versions and check for any updates or patches that fix the generation issue.
Explore a Free Demo of – Automated E-invoice Software for Easy Compliance
Summary in Key points
Here is a summary of GSTR-9C in bullet points:
- GSTR-9C is a reconciliation statement that must be filed annually along with the GSTR-9 return in India under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime.
- The reconciliation statement certifies the accuracy and completeness of the data declared in the annual return (GSTR-9) and the taxpayer’s books of accounts.
- The certification must be done by a Chartered Accountant or a Cost Accountant.
- The due date for filing GSTR-9 and GSTR-9C is December 31st of the next financial year for which the return is being filed.
- Inaccurate reconciliation can result in penalties and legal consequences.
- Accurate reconciliation helps ensure the correctness and completeness of the information declared in the return and the taxpayer’s books of accounts.
- The reconciliation statement and certification assure the Indian government that the data declared in the return is accurate and that the reconciliation has been appropriately conducted.
- GST Rates for ProductsGST Rates: mixer grinder GST rate GST on labour charges GST on solar panel crockery GST rate GST on lpg cylinder GST on vehicles GST on water tanker fish GST rate GST on cigarettes gst on dental services GST on healthcare services GST on sports academy GST on advertisement GST for real estate GST on emi GST rate for construction services GST on maintenance charges coconut broom GST rate tent house GST rate GST on import goods
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is a JSON error in GSTR-9C filing?A JSON error occurs when the file generated for GSTR-9C has issues in its structure, format, or content that prevent it from being successfully uploaded to the GST portal.
- Why do I encounter a “File Corrupted” JSON error in GSTR-9C?This error happens when the file is damaged or incomplete, often due to a network or software issue during generation or uploading.
- What does the “Invalid Format” JSON error mean in GSTR-9C filing?It indicates that the structure or content of the JSON file does not conform to the required specifications for GSTR-9C on the GST portal.
- How can I resolve the “Mismatch in Data” JSON error while filing GSTR-9C?Reconcile the data in GSTR-9C and GSTR-3B to ensure they match before uploading the JSON file.
- What causes the “Error in Digital Signature Validation” during JSON upload?This error is caused when the Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) used is invalid, expired, or improperly configured.
- Why am I getting a “File Upload Failed” JSON error on the GST portal?This is usually due to network issues, server timeouts, or file size limits. Retry the upload after some time or check your internet connection.
- What is the “Field Length Exceeded” JSON error in GSTR-9C?This error occurs when data entered into a field exceeds the allowed character limit for that field in the JSON file.
- What should I do if I encounter the “JSON File Not Readable” error on the GST portal?Check if the JSON file is correctly formatted and generated. If not, regenerate the file and try uploading again.
- How can I avoid errors while generating the JSON file for GSTR-9C?Use the latest version of GST return software, ensure data accuracy, and double-check file compatibility with the portal before generating the JSON file.

